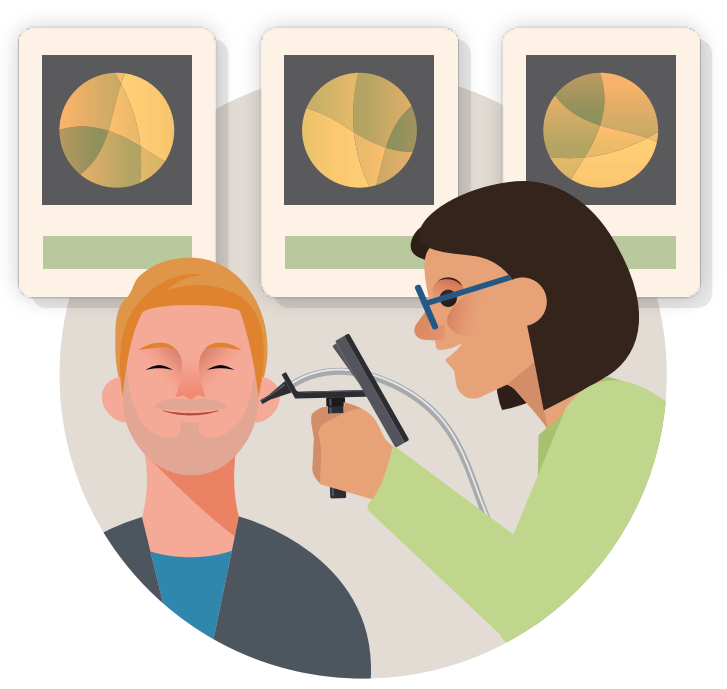
Microsuction
Micro-suction is considered by medical experts to be the Gold Standard procedure for removing earwax and improving your hearing
Micro-suction is quick, safe, and a painless treatment by gently suctioning wax from the ear
During the process high definition images and videos are taken to help you to clearly visualise and understand a diagnosis
Examinations can be digitally shared with ENT specialists for further evaluation
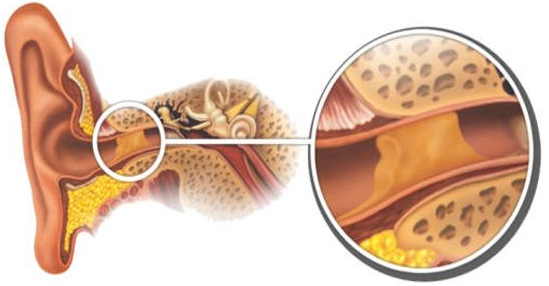
What is Ear Wax?
Ear wax (cerumen) is a natural yellow/ brown substance secreted by the sebaceous and cerumenous glands in the layer of skin lining the ear canal. Ear wax is believed to have 3 main health benefits:
Cleans the ear canal by trapping and capturing dead skin , small foreign objects (e.g. insects) and any dust or dirt roaming in the environment
Lubricates the layer of skin lining the ear canal preventing it from drying out and becoming cracked
Protects the ear canal/ eardrum and reduces the risk of fungi and bacterial ear infections due to it being slightly acidic and possessing antibacterial properties
In most people ear wax will naturally migrate outwards of the ear canal, however, in some cases ear wax can build up and become impacted.
Causes of impacted wax
In some cases ear wax can have a tendency to build up and become compacted. There are many factors that can cause this.
Ear wax doesn’t naturally migrate outwards due to an abnormal layer of skin lining the ear canal
the ear canal is very narrow causing the ear wax to become impacted
the ear canal has bony protrusions (exostosis) blocking the wax inside
the ear wax is pushed deep into the ear canal through the use of cotton buds
excessive hair (cilia) is present in the ear canal that traps the wax and prevents it from escaping out
the ear wax is dry and hard (more common with age) which makes it more difficult for it to migrate outwards
a worn hearing aid or earplug obstructs the natural migration path of ear wax
Symptoms of impacted wax?
The most common symptom caused by impacted ear wax is a ‘blocked ear’. The sensation of a blocked ear is due to the wax creating a “plug” inside the ear canal. A plug of wax can lead to the following symptoms:
Feeling of fullness and dullness;
temporary hearing loss;
internal sounds being louder(e.g. chewing, breathing, own voice)
earache (otalgia) and discomfort
ringing in the ear (tinnitus) mild vertigo (sensation of the room spinning)
cough - due to excessive pressure created by the ear wax stimulating the facial nerve inside the middle ear
whistling (acoustic feedback) of hearing aid
itchiness/ irritation of the ear canal